- source: CentryMed
- author: CentryMed
-
2025.07.23
October 18, 2024 — On October 18, 2024, the Investigational New Drug (IND) application for the Phase II clinical trial of CentryMed’s DNV3 Injection combined with toripalimab and chemotherapy has received implied approval from the National Medical Products Administration (NMPA). The trial is intended for the treatment of melanoma patients who have failed systemic therapy. This marks CentryMed’s 10th clinical approval.
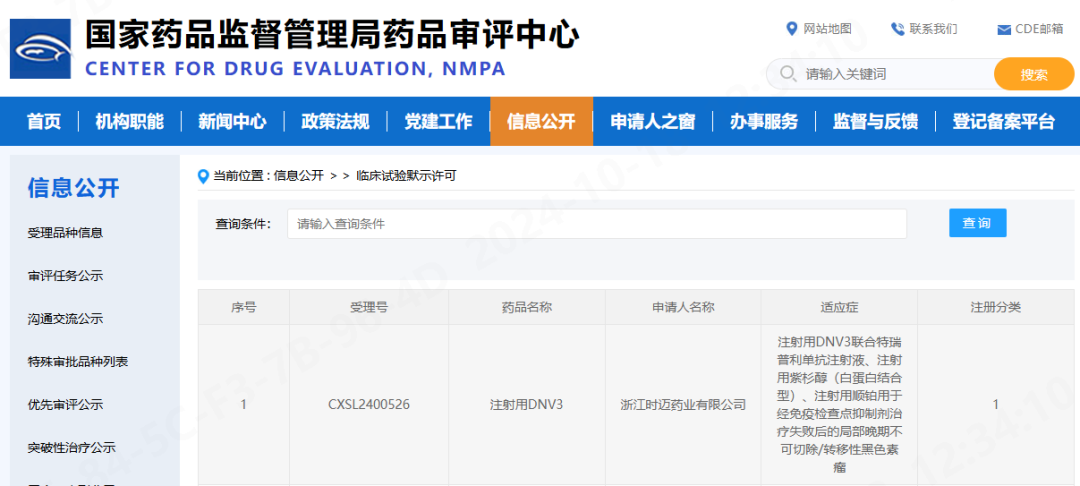
DNV3 is a recombinant fully human monoclonal antibody targeting lymphocyte activation gene-3 (LAG-3). It is a Class 1 biological drug independently developed by CentryMed for anti-tumor therapy and represents one of the most promising immune checkpoint inhibitor monoclonal antibodies following PD-1/PD-L1. Preclinical and clinical data show that DNV3 has excellent potential to reverse PD-1/PD-L1 resistance.
Registration clinical data from CentryMed’s DNV3 combined with toripalimab in melanoma treatment demonstrated that the dual immunotherapy combination produced excellent clinical efficacy in patients who had previously failed immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy.
The newly approved clinical trial will evaluate the combination of DNV3 and toripalimab with the addition of low-dose chemotherapy during the initial treatment course. The chemotherapy regimen aims to induce immunogenic cell death in tumor cells, establishing a more favorable immune microenvironment, further enhancing the efficacy of immunotherapy, and improving patient tolerance.
Immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy has become a widely used clinical treatment regimen for melanoma. However, the vast majority of patients develop resistance after immunotherapy, and there is a scarcity of available treatments for these resistant patients. This is especially true for patients with acral melanoma and mucosal melanoma, which account for a larger proportion in China, creating significant unmet clinical needs for later-line treatment options.
We believe this clinical exploration of the combination therapy regimen will bring better treatment choices and clinical benefits to this patient population.